The Metaverse: How the Next Big Wave in Technology is Attracting Long-Term Investments
The Metaverse is growing in popularity, with the market opportunity estimated to reach USD800 billion globally by 20241. But what exactly is the Metaverse and why is it gaining so much interest with investors?
To better understand the development of this new ecosystem, let’s go back to the beginning and explore the evolution of the internet. For the last three decades, advancements in technology have redefined the way we live and the way we interact with one another.
Source: HSBC Private Bank, March 2022
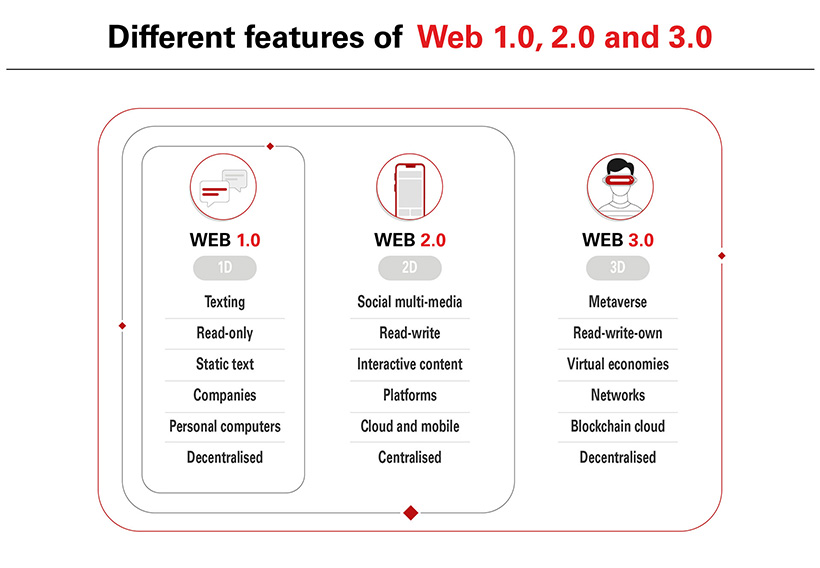
Web 1.0 - In the early 1990s, the first generation of the world wide web was a one-dimensional form of communication where users could search for information and view it. Known as the “Read-Only Web”, it allowed individuals and companies to publish HTML webpages, presenting users with a static online experience similar to viewing a simple catalogue or a brochure2.
Web 2.0 – In the early 2000s, the new phase of the internet allowed users to contribute their own content and interact with one another. Known as the “Social Web” or the “Read-Write web”, users were able to communicate and collaborate in real time through social media, blogs, instant messaging services, podcasts and web applications3. With such a vast amount of content being created and shared, new technology platforms and companies emerged, such as Facebook, Google, Yahoo, Apple and Twitter, who centralised and distributed the data.4
Web 3.0 – With developments in artificial intelligence, machine learning and the onset of 5G, Web 3.0 will completely change the way we create and consume content. Known as “Semantic Web,”5 it allows for users to create, own and control their own data, using blockchain technology, rather than storing it on a centralised database owned by a third-party technology provider, where people can exchange information and make digital transactions securely and transparently.6
Leveraging this new emerging ecosystem, the Metaverse is quickly developing as the next generation of the internet – a decentralised virtual world where our physical and digital realities seamlessly integrate to create new and more immersive experiences, with more freedom and ability to connect effortlessly7.
Will this new virtual world become as important as our real one?
As it is still in its infancy stage of development, the Metaverse may feel like a step back in time for many of its new users in terms of the current aesthetic. However, it is clear that a fundamental shift is already taking place, with brands and businesses exploring new ways of interaction with clients.
Real investments are deployed to support the development of the Metaverse across multiple platforms, in the anticipation that it will transform everyday aspects of our lives creating expanded online markets for industries such as shopping, gaming, e-sports, and experiences. Some companies are going as far as building digital headquarters where employees and consumers can meet in their new virtual spaces.
Even HSBC has recently announced the acquisition of its new virtual land in the Sandbox, the first of its kind in the financial services industry to engage clients and connect with sports, e-sports and gaming enthusiasts in the Sandbox Metaverse.8
HSBC is not alone in this race to capture new opportunities with recent announcements by high profile technology companies outlining their strategies for the future. Meta invested USD10 billion in 2021 alone9 – a real sign of potential market opportunity, confirming that the Metaverse is indeed gaining in importance.
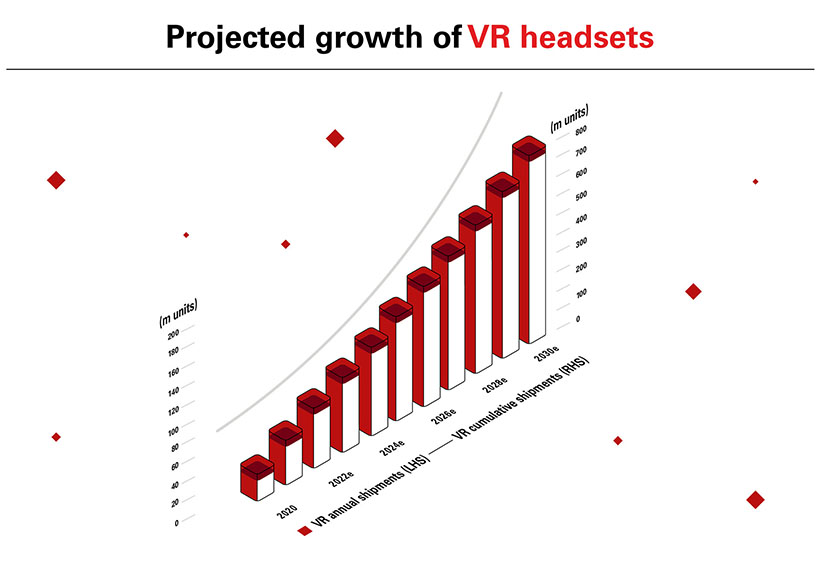
It is no surprise then that consumer data also supports this growing interest with demand for VR devices expected to accelerate in the coming years, comparable with the early years of smartphones, to support the development of Metaverse-based markets for gaming, socialising, and collaboration.
Source: HSBC, www.oculus.com, January 2022
Mirroring the real world, users create and download digital replicas of themselves, known as Avatars, to be their key to exploring and experiencing this new virtual environment, thought to be of infinite possibilities.
We are at the start of a very exciting new journey and these 3D digital experiences are only just the beginning of what the future potential of the Metaverse might hold.
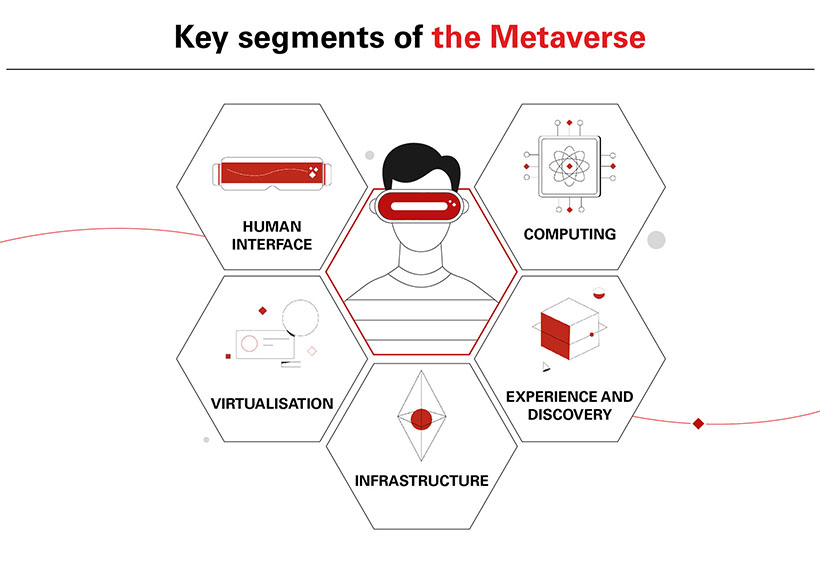
5 key segments for long-term investment
Beyond the headsets and the virtual reality experiences, the Metaverse provides growth opportunities for companies involved in everything from core infrastructure and connectivity through to the delivery of the actual experience and the development of 3D digital content to shape the future of the internet.
At HSBC Private Bank, we see investment opportunities with companies operating across five key market segments.
Source: HSBC Private Bank, February 2022
1. Infrastructure – Servers, data centres and cloud supply chains will make up the core infrastructure for the Metaverse, as large amounts of data will need to be processed and exchanged. Faster and better data networks via 5G will power and allow for new virtual and augmented reality technology, allowing for real world experiences to be improved by virtual ones. This growth in digitisation and connectivity will require new energy sources and solutions to power this highly energy intensive ecosystem.
2. Computing - Developments in AR/VR and the next generation of quantum computing will enable a more realistic and immersive Metaverse for users. Advanced computation and algorithms will enable parallelisation and the rendering of computer-generated imagery very quickly, outpacing the current graphic processing units (GPUs).
3. Virtualisation - Design tools and spatial scanning software will combine our physical world with virtual ones allowing for completely new client experiences. Product development and manufacturing will benefit from the concept of “digital twins,” a virtual replication of a physical system, allowing them to mirror, analyse, and predict behaviour of their virtual equivalents, providing a real-time view on how a physical asset is performing.
4. Experience & Discovery - 3D digital content will allow users to experience, collaborate, and connect with one another, opening up new worlds for sporting, gaming, shopping, socialising and learning. A “creator economy” is emerging which allows content creators to design experiences and their own digital assets, which can be traded or transferred to digital wallets through Non Fungible Tokens (NFTs).
5. Human Interface - Leading hardware companies, which are developing headsets, wearables and VR/XR interfaces, will be key to transporting us into this new virtual space. Technologies such as sensors and semiconductor chips, which are used in smart phones, 3D glasses, connected watches, and smart audio assistants, will improve allowing VR devices to become lighter, smaller, and easier to integrate into our day to day lives.
What opportunities are available for investors?
While the Metaverse is still in the early stages of its ecosystem development, we believe there is great potential for investors to participate in its long-term future growth.
With a focus on these 5 key market segments, the time is now for the astute investor to learn, to research, and to selectively identify opportunities for long term investment.
At HSBC Private Bank, we are committed to providing timely and innovative solutions to our clients in order to capture secular thematic investment opportunities”, said Lina Lim, Regional Head of Discretionary and Funds, Asia Pacific, HSBC Wealth and Personal Banking.
1 Source: Bloomberg Intelligence, November 2021; Estimate was compiled by Bloomberg, representing a compound annual growth rate of 13.1% (vs 2020 data), based on our analysis and Newzoo, IDC, PWS< Statista and Two Circles Data ↩
2 Source: HSBC Private Bank, March 2022 ↩
3 Source: International Journal of Research and Scientific Innovation (IJRSI) |Volume III, Issue IX, September 2016|ISSN 2321–2705| https://www.rsisinternational.org/IJRSI/Issue31/75-78.pdf ↩
4 Source: HSBC Private Bank, March 2022 ↩
5 Source: “Semantic Web” (as defined by Tim Berner’s Lee) is an extension of the World Wide Web (Web 3.0) through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). ↩
6 Source: HSBC Private Bank, March 2022 ↩
7 Source: HSBC Private Bank, March 2022 ↩
8 Source: HSBC to Become The First Global Financial Services Provider to Enter The Sandbox, March 2022 | The Sandbox, https://sandboxgame.medium.com/hsbc-to-become-the-first-global-financial-services-provider-to-enter-the-sandbox-c066e4f48163 ↩
9 Source: https://www.nytimes.com/2022/02/02/technology/meta-facebook-earnings-metaverse.html ↩